The SuperCDMS Experiment
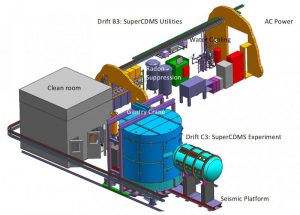
SuperCDMS SNOLAB will be the successor to the previous generation of CDMS experiments, which were located deep underground in the Soudan mine in Minnesota, USA. SNOLAB (Vale Inco Mine, Sudbury, Canada) is a much deeper and cleaner facility, providing significantly more shielding from high energy cosmic ray particles and from radioactive decay byproducts. It will include a cryogenics system designed to maintain the detectors at temperatures within a fraction of a degree above absolute zero in order to damp out thermal noise. This will be surrounded by layers of clean shielding materials to exclude radioactive backgrounds from the environment. The detectors located inside the cryostat will be modular and are arranged in towers that provide electrical connections and cooling. Special low-noise electronics will be used to process the detector signals, which will be gathered and stored by data acquisition and computing systems. Some of the detectors will be operated in a way that provides ultra-low energy thresholds while others will provide a precise measurement of backgrounds from normal matter interactions. This increases the chances of having a positive identification of dark matter particles or will allow much more stringent limits to be placed on the interaction of these elusive particles with normal matter.